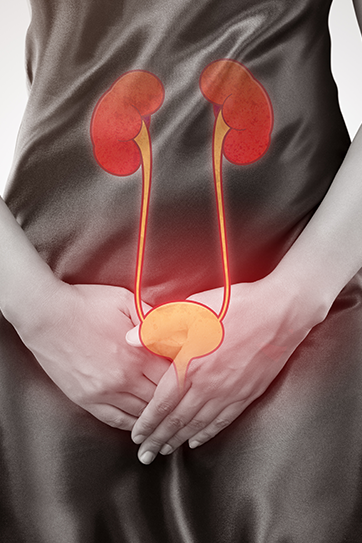
Bladder cancer is a type of cancer that develops on the surface of the bladder and typically arises in the urinary tract.
The bladder, an organ responsible for storing and subsequently expelling urine, is part of the human urinary system. It is a flexible muscular organ that facilitates the temporary storage of urine.
For the bladder to function properly, it requires complex coordination between nerves and muscles. Disorders of bladder function or issues such as bladder cancer can lead to various health problems related to urine. Regular health check-ups and consultations with specialist physicians are important for maintaining bladder health.
Bladder cancer usually results from a combination of specific risk factors and genetic elements. The key factors influencing the development of this cancer include:
A combination of these factors may contribute to the onset of bladder cancer. However, everyone's situation is unique, and the impact of these factors can vary from individual to individual. Making healthy lifestyle choices, regular health check-ups, and conscious management of risk factors can help reduce the risk of bladder cancer.
Bladder cancer is a disease that includes various types originating from different cell types. The most common type is transitional cell cancer, referred to as urothelial cancer. This type of cancer originates from cells lining the inner surface of the bladder and can spread to other areas of the urinary tract.
Additionally, squamous cell cancer is one of the types of bladder cancer and tends to exhibit an aggressive course. Adenocarcinoma, on the other hand, originates from glandular (gland-like) cells lining the bladder mucosa and is a rarer type. Sarcoma originates from the muscle layer of the bladder. Although it is rarer than other types of bladder cancer, it often shows a more aggressive course.
Each type of bladder cancer has specific characteristics and treatment approaches. Determining the type of cancer in the diagnosis plays a crucial role in formulating an appropriate treatment plan. Taking into account factors such as the stage, size, and other considerations, doctors determine disease-specific treatment strategies.
Diagnosing bladder cancer typically involves a series of diagnostic tests. These tests are based on factors such as the patient's symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. Urography is used to obtain X-ray images of the bladder and urinary tract. This test, conducted with a colored substance, can help identify abnormal areas within the bladder.
Cystoscopy is a test performed by inserting a device with a camera into the bladder through a flexible tube. With this method, the doctor can examine the inner surface of the bladder and observe potential abnormal cells. Urine tests are used to determine the presence of bladder cancer, especially to detect blood or abnormal cells in the urine.
Imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help in a detailed examination of the bladder and surrounding tissues. These diagnostic methods assist doctors in assessing bladder cancer and formulating appropriate treatment plans. However, each patient may be different, and doctors determine the most suitable diagnostic strategy by considering the patient's specific condition.
The treatment of bladder cancer typically involves surgical operations. These operations may include transurethral resection (TUR) and radical cystectomy. TUR aims to remove tumors within the bladder using an endoscopic method. Radical cystectomy involves the surgical removal of the entire bladder or a portion of it.
In addition, partial cystectomy or segmental cystectomy are other surgical procedures used in the treatment of bladder cancer. In this procedure, only the part of the bladder containing the tumor is removed, and efforts are made to preserve the remaining healthy bladder tissue. This method can be preferred in cases where the cancer is limited and does not require the removal of the entire bladder.
During partial cystectomy, the surgeon identifies and removes the region where the tumor is located, and then corrects the remaining portion to preserve healthy bladder tissue. This procedure can help maintain bladder function and urine control, especially in cases with small tumors or a limited number of tumors.
Neobladder reconstruction is also a surgical procedure included in bladder cancer cases. In this procedure, a "reconstructed bladder" is created in the body after the removal of the bladder. The purpose of this new structure is to allow the patient to hold urine and function like normal urinary functions. During this procedure, the surgeon typically uses the small intestine to create an artificial bladder. The intestinal segment is arranged as a pouch or reservoir and placed inside the body. This artificial bladder allows the storage of urine and controlled emptying. For detailed information on bladder cancer, contact Medwide.



Get practical information about the topics you are most curious about. Everything you need to make informed decisions on your beauty and health journey is here with all the details from A to Z.
Bladder cancer typically first develops within the bladder. In other words, cancer cells usually originate in the inner layers of the bladder wall and can grow over time. However, in advanced stages, cancer cells can metastasize to surrounding tissues or lymph nodes.
Bladder cancer is a serious disease that requires treatment. However, the prognosis can vary depending on the patient's condition, the stage of the cancer, the extent of spread, and the response to treatment.
The question of whether bladder cancer can be completely cured depends on the patient's condition and the stage of the cancer. Bladder cancer detected in early stages can be successfully treated, contributing to maintaining the patient's quality of life. However, the chance of recovery may decrease in advanced stages or cases with metastasis.
Medwide meticulously arranges airport transfers for patients and their companions, ensuring their comfort and satisfaction.
Medwide's VIP transfer service offers patients a personalized and privileged travel experience, providing exceptional service.
Medwide transports patients and their companions comfortably and luxuriously, making their journeys enjoyable and relaxing.
Medwide offers quality healthcare services to patients at affordable prices, ensuring transparency and fairness in costs.
Medwide provides fast treatments by reducing patient wait times, our expert doctors promptly respond to our patients' needs.